
Breadcrumb
- Home
- Labs
- Advanced Labs
- Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and Star Clusters
- Part 2: Star Clusters
Part 2: Star Clusters
Globular and Open Star Clusters
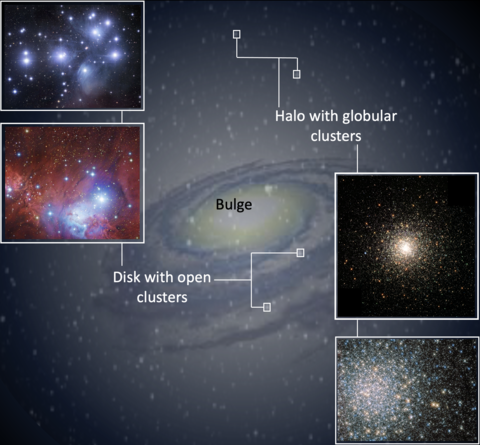
(M80), HST/NASA/ESA (M5), Subaru Telescope (NAOJ)/DSS/Robert
Gendler (NGC 2264), Robert Gendler (Pleiades)
H-R Diagrams of Star Clusters
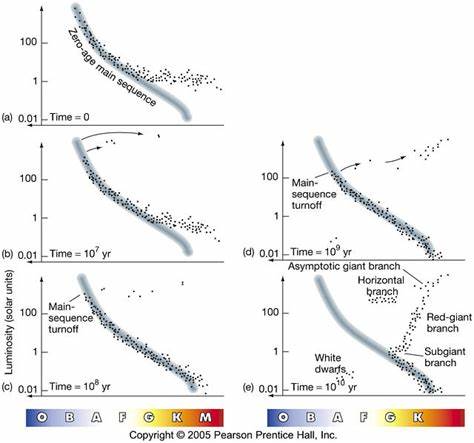
We can use the HR Diagram of a Star Cluster to approximate its age. This is done using the turn off point (TP), or the point in which stars start evolving off the main sequence after exhausting their main source of fuel. This evolution will start with the brightest stars, which have the shortest lifetimes. See the diagram below for more detail on this process over time.
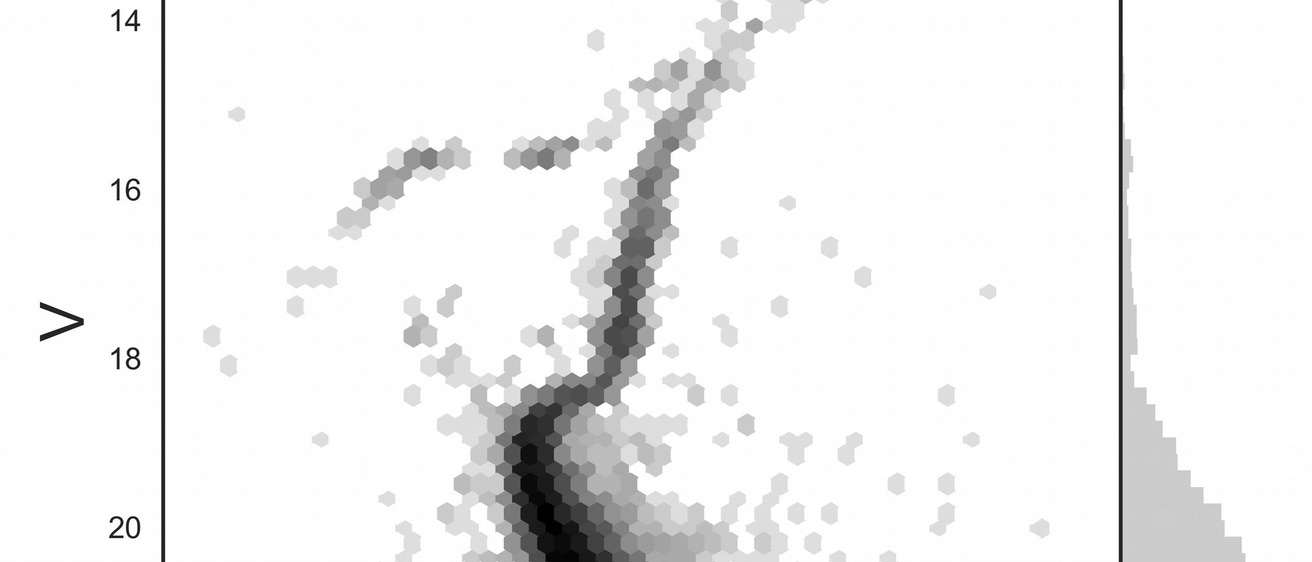
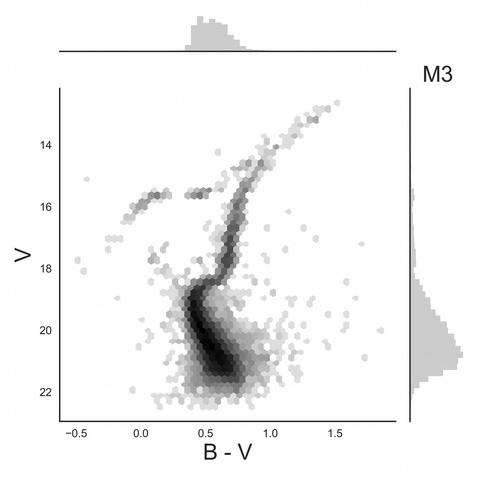
Now using this knowledge, examine the HR diagram for the globular cluster M3 and try to identify the main sequence (MS), the main sequence turnoff point (TP), the giant branch (GB), the horizontal branch (HB)
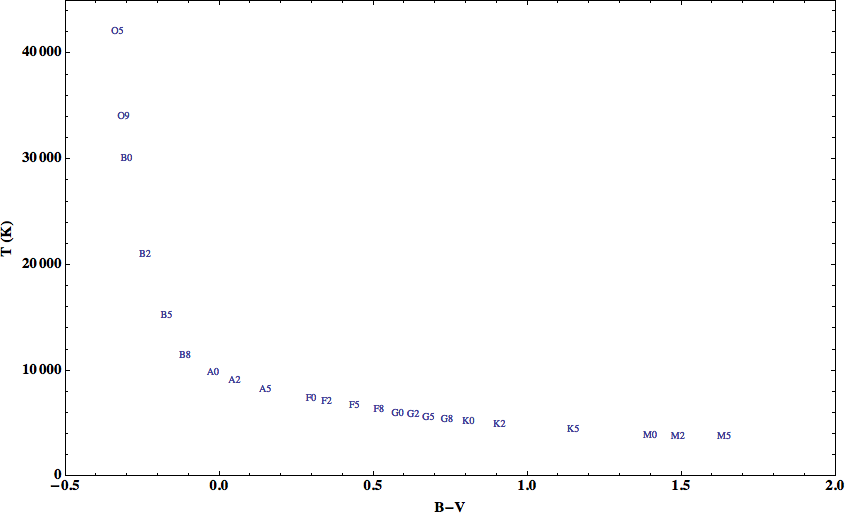
Spectral Types as a Function of Color
The temperature or spectral type of a star can be calculated as a function of its B - V color index. Astronomers use Ballestero's Formula to do this. But for our purposes, we can infer the spectral type from the B - V color index using the plot below, which serves as a good "by eye" approximation. This plot also indicates the turn off point (TP), or the B-V magnitude at which each spectral type will evolve off the main sequence.
Age of a Star Cluster
The main sequence turn off age tells us how old the cluster is. The mass of a star sets the luminosity, the temperature, the size, and how fast it will evolve off of the main sequence: stars of the same mass will evolve at the same rate. Listed below are the main sequence luminosities and life times of stars.
| Spectral Class | Luminosity | Time on Main Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| O | 104 LSUN | < 107 years |
| B | 103 LSUN | 107 < t < 109 years |
| A | 101 LSUN | 109 years |
| G | 100 LSUN | 1010 years |
| K | 10-1 LSUN | 1011 years |
H-R Diagrams of Individual Star Clusters
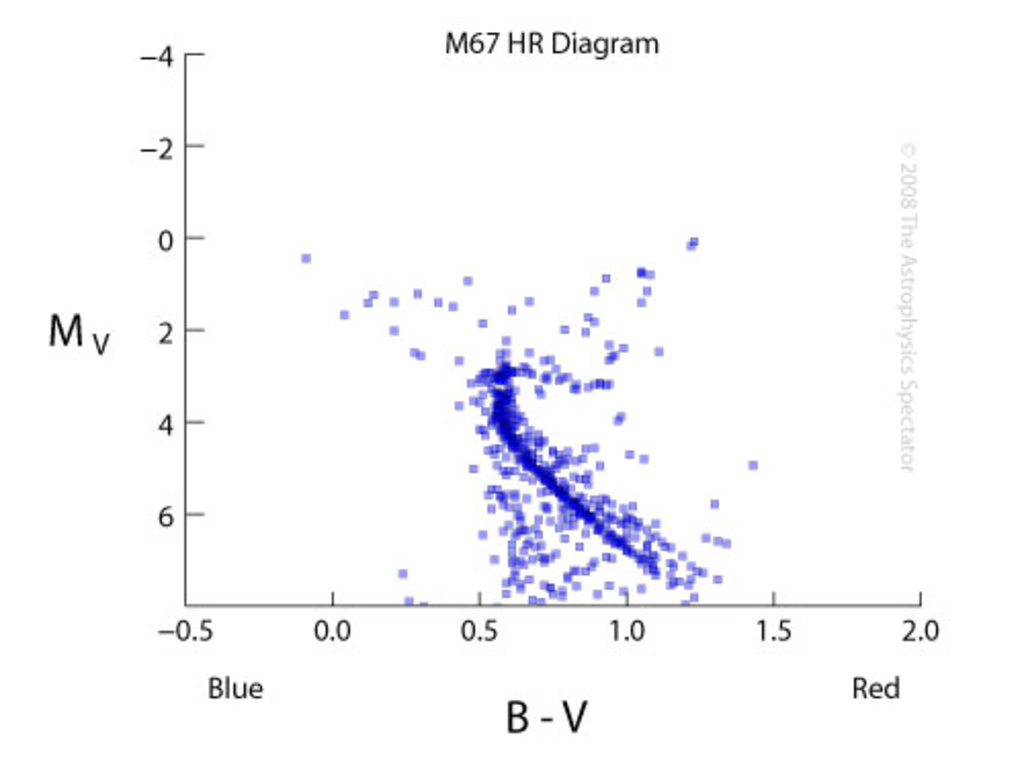
Open Star Cluster M67, Stassun et al., 2002, A&A 382, 899
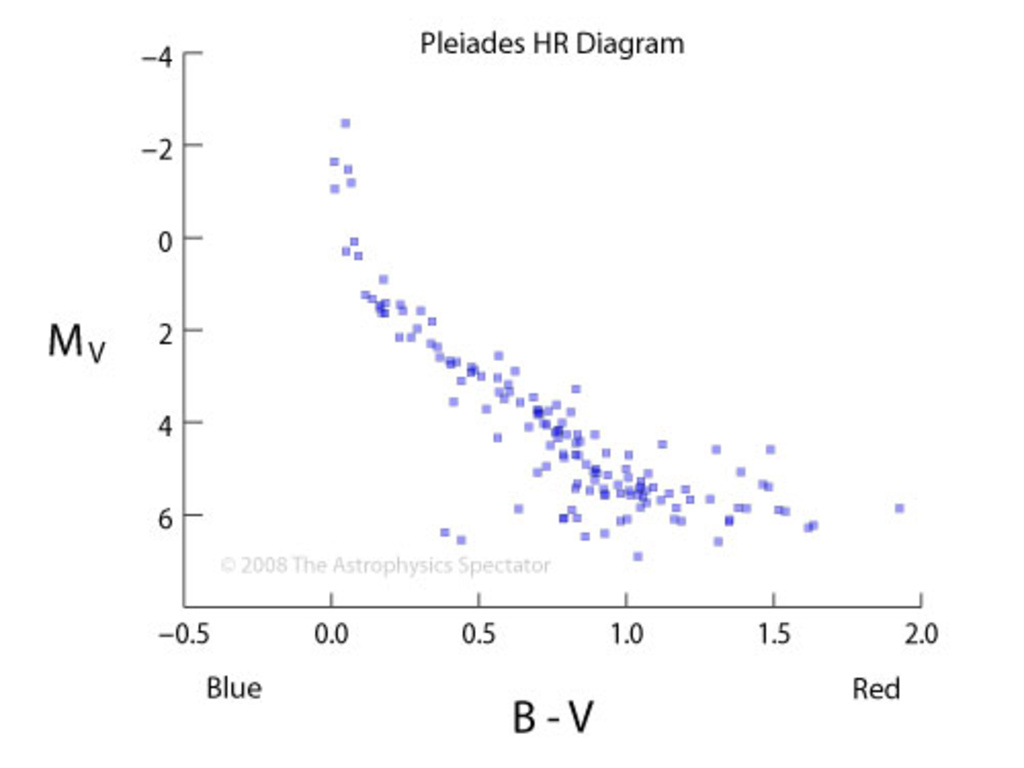
Open Star Cluster Pleiades, Kharchenko et al., 2004 A&A 438 1163
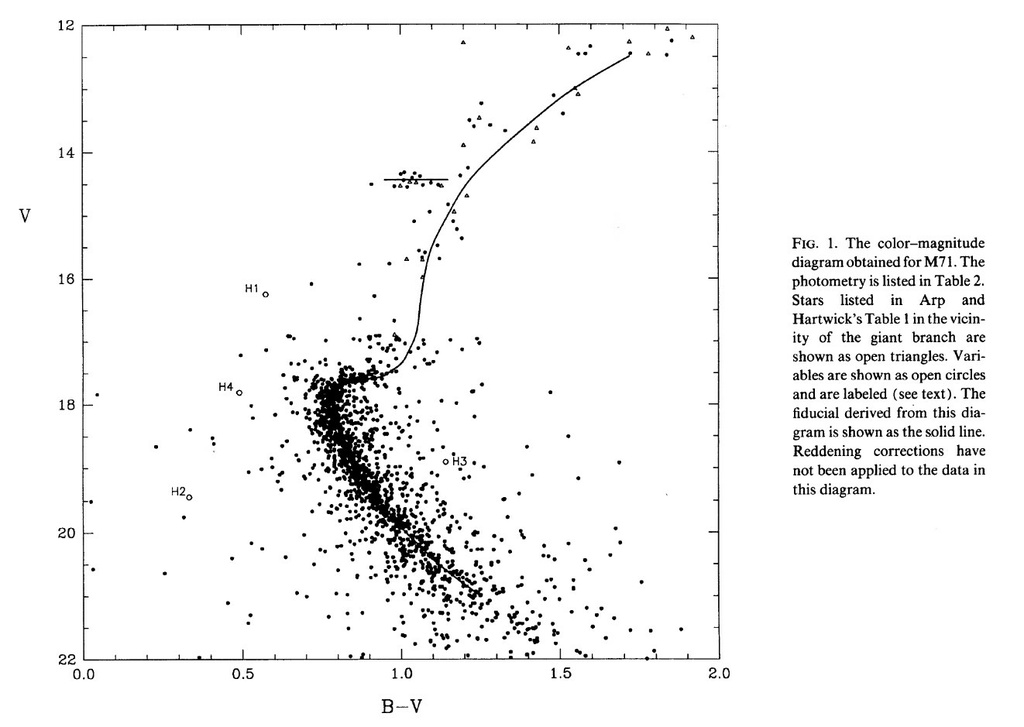
Globular Star Cluster M71, Hodder et al. AJ 1992, 103 460
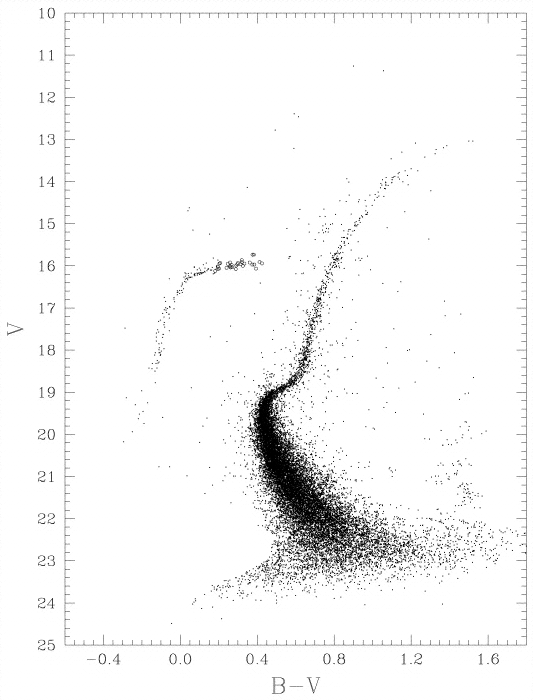
Globular Star Cluster M2, Lee & Carney, ApJ 1999 117 6
A Final Word on Reddening
Reddening (interstellar extinction) is the preferential scattering and absorption of "bluer" EM radiation by dust and gas along the observer's line of sight to an object. This can be quantified in color index by independent methods and used to calculate the intrinsic (i.e. unaltered) color of the astronomical source via the equation:
(B-V)intrinsic = (B-V)observed - E(B-V)
Notice that a positive extinction makes the intrinsic color of the source "bluer".