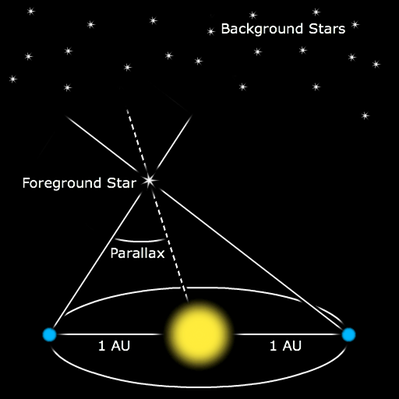
Parallax is the observed apparent change in the position of an object resulting from a change in the position of the observer. Specifically, in the case of astronomy it refers to the apparent displacement of a nearby star as seen from an observer on Earth.
The parallax of an object can be used to approximate the distance to an object using the formula:
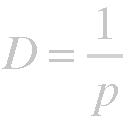
Where p is the parallax angle observed, and D is the actual distance measured in parsecs. A parsec is defined as the distance at which an object has a parallax of 1 arcsecond. This distance is approximately 3.26 light years.
Example Question
The bright star Vega has a parallax of 0.129", how far is it?
Solution
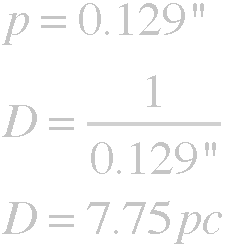
So Vega is about 7.75 parsecs from Earth, or about 25 light years.