
Breadcrumb
- Home
- Labs
- Observational Labs
- Observing Lunar Features
- Part 1: Physics of Impacts and Barringer Crater
Part 1: Physics of Impacts and Barringer Crater

Meteorites
Your instructor will show you a number of meteorite samples and will describe their origins and properties. What similarities do you see among the samples? What differences?
Impact Demonstration
Your instructor will demonstrate a meteor impact simulation using a large tray of flour and a "meteoroid". Describe the shape of the crater produced, as well as any unusual features. How do you think this compares to actual impact features on Earth or the Moon?

About the Barringer Crater
Barringer Crater (also known as Meteor Crater) is a meteorite crater located 70 kilometers from Flagstaff, Arizona. Barringer was the first crater to proven to be the result of an impact, and remains one of the world's most well preserved impact sites.
The crater stretches 1200 meters across and 170 meters deep, with the rim of the crater rising 45 meters above the surrounding landscape. The area around the impact site is tinted red with oxidized iron from the nickel-iron meteor which impacted there almost 50,000 years ago.
Geologist Daniel Barringer, who first suggested that the crater was the result of an impact, was also a wealthy investor in mining operations. Not realizing that the energy released by the impact would have destroyed most of the meteor, Barringer spent 25 years and hundreds of thousands of dollars mining the center of the crater in search of what he believed was an iron meteor worth billions of dollars. Barringer died of a heart attack in 1929, shortly after reading conclusive evidence that there was no meteor to be found and realizing that he had bankrupted himself searching for it.
Exercises
Impact:Earth! Is an application developed by Purdue University which approximates the resulting crater and after effects of an impact based on different selections of mass, velocity, impact angle, etc.
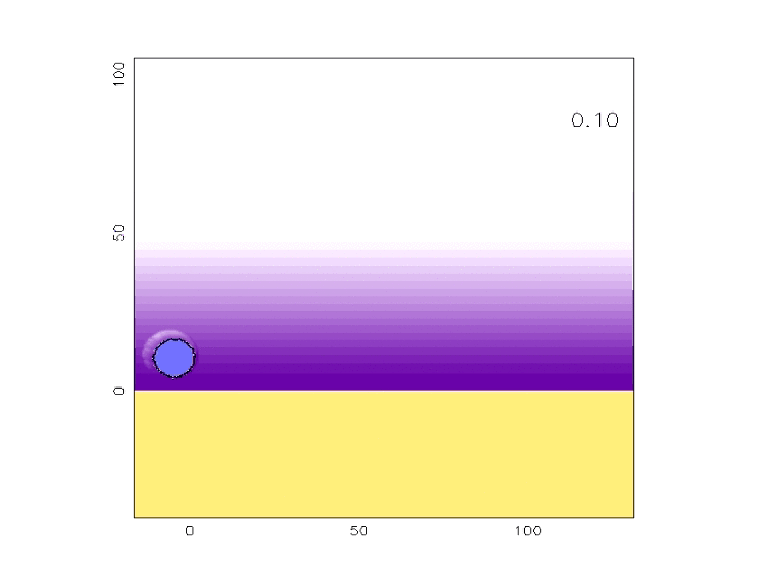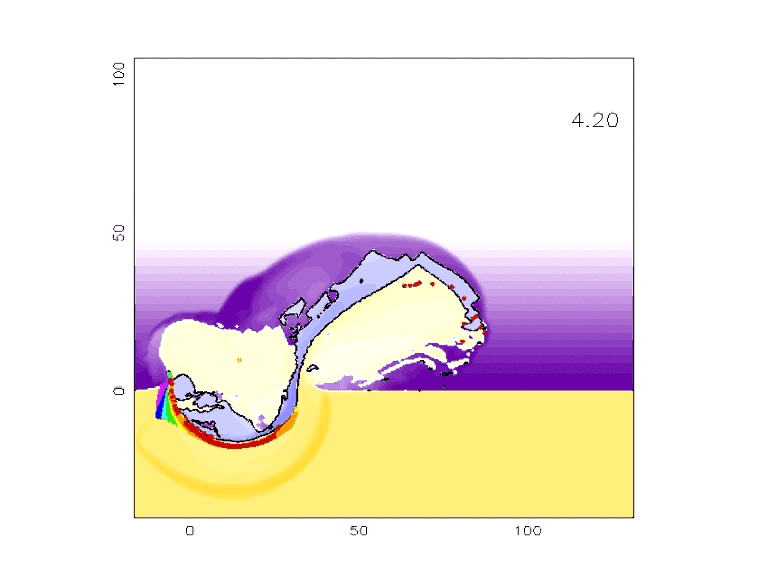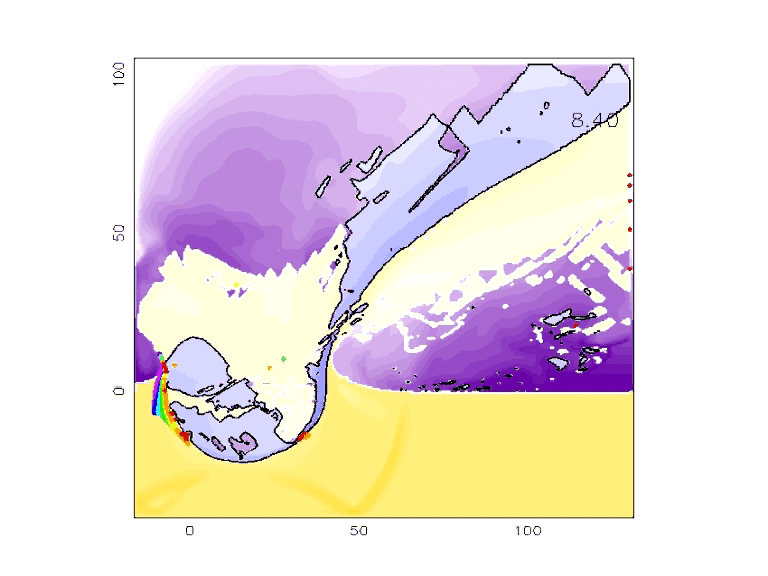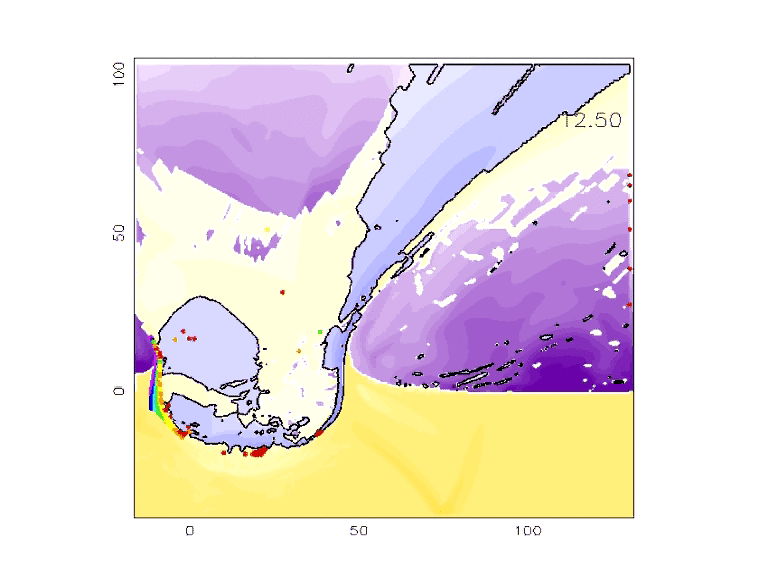
- Using the application, work with your team to produce a crater whose dimensions closely match those of the Barringer Crater. (Hint - You can reduce the number of variables by looking at what you know about the impact site and the impacting object.
Guideposts
- While not true for all impacts, the typical impact angle for objects impacting the Earth is 45 degrees.
- Both Arizona and Iowa are dominated by sedimentary rock, not crystalline rock.